Instruments that deal with diagrams as code, akin to PlantUML, are invaluable for speaking
complicated system habits. Their text-based format simplifies versioning, automation, and
evolving architectural diagrams alongside code. In my work explaining distributed
methods, PlantUML’s sequence diagrams are notably helpful for capturing interactions
exactly.
Nevertheless, I typically wished for an extension to stroll via these diagrams step-by-step,
revealing interactions sequentially reasonably than exhibiting your entire complicated move at
as soon as—like a slideshow for execution paths. This want displays a typical developer
situation: wanting personalised extensions or inner instruments for their very own wants.
But, extending established instruments like PlantUML typically entails vital preliminary
setup—parsing hooks, construct scripts, viewer code, packaging—sufficient “plumbing” to
deter speedy prototyping. The preliminary funding required to start can suppress good
concepts.
That is the place Massive Language Fashions (LLMs) show helpful. They will deal with boilerplate
duties, liberating builders to deal with design and core logic. This text particulars how I
used an LLM to construct PlantUMLSteps, a small extension including step-wise
playback to PlantUML sequence diagrams. The purpose is not simply the device itself, however
illustrating the method how syntax design, parsing, SVG era, construct automation,
and an HTML viewer have been iteratively developed via a dialog with an LLM,
turning tedious duties into manageable steps.
Diagram as code – A PlantUML primer
Earlier than diving into the event course of, let’s briefly introduce PlantUML
for many who is perhaps unfamiliar. PlantUML is an open-source device that enables
you to create UML diagrams from a easy text-based description language. It
helps
numerous diagram varieties together with sequence, class, exercise, element, and state
diagrams.
The ability of PlantUML lies in its capacity to model management diagrams
as plain textual content, combine with documentation methods, and automate diagram
era inside improvement pipelines. That is notably helpful for
technical documentation that should evolve alongside code.
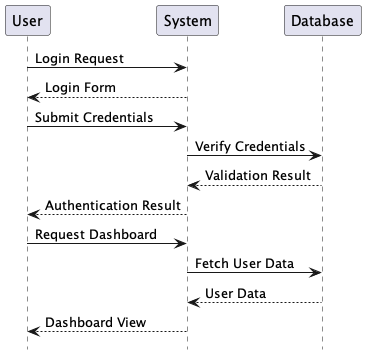
Here is a easy instance of a sequence diagram in PlantUML syntax:
@startuml cover footbox actor Consumer participant System participant Database Consumer -> System: Login Request System --> Consumer: Login Type Consumer -> System: Submit Credentials System -> Database: Confirm Credentials Database --> System: Validation Consequence System --> Consumer: Authentication Consequence Consumer -> System: Request Dashboard System -> Database: Fetch Consumer Knowledge Database --> System: Consumer Knowledge System --> Consumer: Dashboard View @enduml
When processed by PlantUML, this textual content generates a visible sequence diagram exhibiting the
interplay between parts.
The code-like nature of PlantUML makes
it straightforward to be taught and use, particularly for builders who’re already snug
with text-based instruments.
This simplicity is what makes PlantUML an ideal candidate for extension. With the
proper tooling, we are able to improve its capabilities whereas sustaining its text-based
workflow.
Our purpose for this undertaking is to create a device which may divide the
sequence diagram into steps and generate a step-by-step view of the diagram.
So for the above diagram, we should always be capable to view login, authentication and
dashboard
steps one after the other.
Step 2: Constructing the Parser Logic (and Debugging)
“Now we have to parse the plantuml information and separate out step. At any time when we
encounter a step marker, we create a step object and preserve including the following strains
to it till we encounter one other step marker or finish of file. In case we
encounter one other step counter, we create new step object, it ought to have all
the contains, actors and contributors from the earlier step. It must also
have all of the content material of the earlier step, until the step metadata has
‘newPage’ attribute. If there aren’t any step markers encountered, which is the case
the place we have now information with out steps, it ought to create a default step. Create a
StepParser to parse given puml information and create checklist of steps.”
Claude generated the preliminary code for a StepParser class and a Step mannequin class to
deal with parsing PlantUML information with step markers. The preliminary implementation had some
logical points:
- Incorrect dealing with of step content material inheritance when newPage attribute was false
- Improper dealing with of declarations (actors, contributors) showing earlier than the
first step marker - Points with making a default step for information with out markers
The Cursor editor was operating in Agent mode, so after operating assessments and figuring out
these points via the failure messages, Claude offered a corrected model that
correctly dealt with:
- Content material collected earlier than step one marker
- Inheritance of content material from the instantly previous step
- World monitoring of declarations throughout steps
- Correct creation of a default step for information with out markers
With these corrections, the parser efficiently handed all assessments.
The following step was to generate a gradle process.
We’d like gradle process which may course of puml information in src/diagrams and its sub
folders. For every file it ought to create a listing with the title of the file the place
it generates legitimate puml file for every step. It will possibly generate that by simply including
@startuml at the beginning and @enduml on the finish of the step content material.
I am going to assist you to create a Gradle process to course of PlantUML information and generate
step-by-step diagrams. First, let’s create the duty in
construct.gradle:
// Course of every .puml file within the enter listing and its subdirectories
fileTree(inputDir).embody('**/*.puml').every { pumlFile ->
def relativePath = inputDir.toPath().relativize(pumlFile.toPath()).toString()
def fileName = pumlFile.title.exchange('.puml', '')
def stepOutputDir = new File(outputDir, fileName)
if (!stepOutputDir.exists()) {
stepOutputDir.mkdirs()
}
// Run the generator for this file
javaexec {
classpath = sourceSets.most important.runtimeClasspath
mainClass = 'com.instance.StepDiagramGenerator'
args = [pumlFile.absolutePath, stepOutputDir.absolutePath]
}
Claude additionally helped producing a easy plantuml sequence diagram to check the gradle
process. The identical one which we used in the beginning of the article.
The gradle process wanted a category PlantUMLGenerator which
can generate SVGs for every step.
Cursor within the Agent mode generated the code for the category.
It then ran the construct to confirm the duty.
Let's run a take a look at to substantiate our implementation works: cd /Customers/unmeshjoshi/work/plantumlsequence && ./gradlew clear construct
Job :generateStepDiagrams
Generated step diagram: /Customers/unmeshjoshi/work/plantumlsteps/construct/generated-diagrams/user-authentication/step-01-step-1-user-login.puml
Generated step diagram: /Customers/unmeshjoshi/work/plantumlsteps/construct/generated-diagrams/user-authentication/step-02-step-2-authentication.puml
Generated step diagram: /Customers/unmeshjoshi/work/plantumlsteps/construct/generated-diagrams/user-authentication/step-03-step-3-dashboard.puml
Generated step move abstract: /Customers/unmeshjoshi/work/plantumlsteps/construct/generated-diagrams/user-authentication/abstract.puml
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 543ms
3 actionable duties: 3 executed
Step 3: Producing HTML Viewer for Step Sequence
The following step was to generate a easy HTML viewer that can be utilized to view the step
sequence.
Now we have to generate a HTML viewer for the step information to be proven one after the other.
The HTML viewer can have a view space the place we present the svg picture generated for every
step with the step title within the metadata for that step. We will have subsequent and former
buttons to point out subsequent and former step picture.
I am going to assist you to create an HTML viewer for the step diagrams. We’ll must: Generate
SVG information from the PlantUML information Create an HTML viewer with navigation controls
Replace the Gradle process to generate each PlantUML and SVG information, together with the HTML
viewer First, let’s create a easy HTML template for the viewer:
….
The agent mode found out just a few points with the template however auto-fixed it by
operating some corrective actions.
This setup allowed us to rapidly generate step diagrams from a single PlantUML file,
and consider them in a step-by-step method. So the above diagram might be seen as a
sequence of following steps:
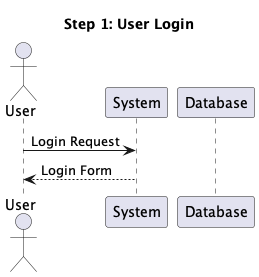
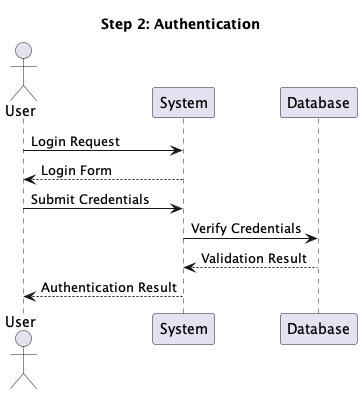
The Code is the Supply of Fact
The place to go from right here?
Whereas the prompts and the LLM assistant (on this case, interacting in an agent-like
mode, using fashions like Claude Sonnet) offered a remarkably efficient solution to
generate a working first model of PlantUMLSteps, it is essential to
acknowledge the character of this generated output.
- Prompts will not be Deterministic: The prompts utilized in our dialog have been
efficient for this interplay, however they can’t be handled as the final word
‘supply of fact’. The identical prompts given to a unique mannequin, and even the identical
mannequin at a later date, will not be assured to provide the very same output due
to the inherent variability in LLM era. - Code Requires Administration: The generated code is the supply of fact for
the device’s performance. As such, it must be handled like some other
software program artifact – checked into model management, reviewed, examined, and
maintained. - Evaluation for Habitability: It is important to revisit the LLM-generated code
after the preliminary creation part. Is it ‘liveable’? That’s, is it moderately
straightforward to learn, perceive, and modify by a human developer? Whereas the LLM helped
overcome preliminary hurdles and boilerplate, making certain the long-term maintainability
and readability of the codebase typically requires human overview and potential
refactoring. The purpose is code that not solely works however can be advanced
successfully over time.
Prompting in pure language (like English) to generate code works nicely within the
early phases of improvement—while you’re exploring concepts, scaffolding performance,
or getting acquainted with a brand new device or framework. However as your system begins to take
form, the boundaries of obscure or broad prompts change into obvious. At this stage, what’s
wanted isn’t extra code era, however conceptual modeling—utilizing the constructs of
your programming language or know-how stack to precisely symbolize the area.
This stage wants deeper considering to construct abstractions, and an alignment between
code construction and area ideas—one thing solely achievable via considerate
design, not simply prompting. If prompt-based code era with out
overview is named “vibe coding,” then the extra disciplined method might be
known as “AI-assisted structured coding.”.
Past Code Technology: The Developer Perception in Refactoring
The following step was to refactor the code to make it extra readable and maintainable.
Initially, the parse technique was an extended, monolithic operate that dealt with every little thing
from
detecting step markers to managing declarations and content material. The code was troublesome
to
perceive and keep.
The complete code is offered in
this preliminary commit on GitHub.
The `StepParser.java` parse technique wants refactoring. It ought to symbolize ideas
used within the requirement or area ideas and observe customary clear code practices
with intentional technique names and code that reads like a DSL.
This preliminary request was open-ended, indicating that the developer acknowledged the
want for enchancment however was searching for steerage on tips on how to method it.
The LLM responded with a complete refactoring that launched a number of new
lessons and strategies:
- Launched `PlantUmlDocument` to symbolize the doc being parsed
- Smaller, extra targeted strategies with intention-revealing names
- Higher encapsulation of associated behaviors
- Extra expressive variable and technique names
/**
* Represents a PlantUML doc being parsed, managing state throughout parsing
*/
non-public class PlantUmlDocument {
non-public remaining Checklist steps = new ArrayList();
non-public remaining Checklist declarations = new ArrayList();
non-public remaining Checklist contentBeforeFirstStep = new ArrayList();
non-public Step currentStep = null;
non-public boolean hasStepMarkers = false;
public void beginNewStep(StepMetadata metadata) {
hasStepMarkers = true;
// Save the present step if it exists
if (currentStep != null) {
steps.add(currentStep);
}
// Create a brand new step
currentStep = new Step(metadata.getName(), metadata.isNewPage(), metadata.getAttributes());
// Add all declarations to the brand new step
currentStep.addAllDeclarations(declarations);
// If this is not a brand new web page and we have now earlier steps, copy all content material from earlier steps
if (!metadata.isNewPage() && !steps.isEmpty()) {
carryOverPreviousStepsContent();
}
}
non-public void carryOverPreviousStepsContent() {
for (Step previousStep : steps) {
for (String contentLine : previousStep.getContent()) {
currentStep.addContent(contentLine);
}
}
}
public void addDeclaration(String line) {
declarations.add(line);
if (currentStep != null) {
currentStep.addDeclaration(line);
} else {
contentBeforeFirstStep.add(line);
}
}
public void addContentLine(String line) {
if (currentStep != null) {
currentStep.addContent(line);
} else if (!line.trim().isEmpty()) {
contentBeforeFirstStep.add(line);
}
}
public void finalizeDocument() {
// Add the final step if it exists and hasn't been added but
if (currentStep != null) {
steps.add(currentStep);
}
}
The complete code is offered in
this commit on GitHub.
The `contentBeforeFirstStep` in `PlantUmlDocument.java` is used just for creating
default step when there aren’t any step markers?
So we are able to presumably
do two go processing the place we first verify if there are step markers.. if there
are.. we do step-based processing. Or else we simply create a default step and add all
declarations and content material. That can take away the necessity to have `contentBeforeFirstStep`
We will additionally possibily title PlantUmlDocument as `ParsedPumlFile` which represents
the parsed puml file.
The LLM applied this suggestion with a two-pass method. It additionally renamed the
PlantUmlDocument as ParsedPumlFile.
The complete code is offered in
this commit on GitHub.
`ParsedPumlFile` might be higher represented as builder sample.
`StepBuilder` generally is a builder for `Step` objects.
This perception demonstrated the developer’s capacity to acknowledge design patterns,
noting that the refactored class adopted the Builder sample.
The ultimate refactoring represents a major enchancment over the unique code:
class StepBuilder {
non-public remaining Checklist steps = new ArrayList();
non-public remaining Checklist globalDeclarations = new ArrayList();
non-public Step currentStep = null;
public void startNewStep(StepMetadata metadata) {
if (currentStep != null) {
steps.add(currentStep);
}
currentStep = new Step(metadata);
currentStep.addAllDeclarations(globalDeclarations);
if (!metadata.isNewPage() && !steps.isEmpty()) {
// Copy content material from the earlier step
Step previousStep = steps.get(steps.dimension() - 1);
for (String contentLine : previousStep.getContent()) {
currentStep.addContent(contentLine);
}
}
}
public void addDeclaration(String declaration) {
globalDeclarations.add(declaration);
if (currentStep != null) {
currentStep.addDeclaration(declaration);
}
}
public void addContent(String content material) {
// If no step has been began but, create a default step
if (currentStep == null) {
StepMetadata metadata = new StepMetadata("Default Step", false, new HashMap());
startNewStep(metadata);
}
currentStep.addContent(content material);
}
public Checklist construct() {
if (currentStep != null) {
steps.add(currentStep);
}
return new ArrayList(steps);
}
}
The complete code is offered in
this commit on GitHub.
There are extra enhancements doable,
however I’ve included just a few to reveal the character of collaboration between LLMs
and builders.
Conclusion
Every a part of this extension—remark syntax, Java parsing logic, HTML viewer, and
Gradle wiring—began with a targeted LLM immediate. Some elements required some knowledgeable
developer steerage to LLM, however the important thing profit was with the ability to discover and
validate concepts with out getting slowed down in boilerplate. LLMs are notably
useful when you have got a design in thoughts however will not be getting began due to
the efforts wanted for organising the scaffolding to strive it out. They can assist
you generate working glue code, combine libraries, and generate small
UIs—leaving you to deal with whether or not the thought itself works.
After the preliminary working model, it was necessary to have a developer to information
the LLM to enhance the code, to make it extra maintainable. It was essential
for builders to:
- Ask insightful questions
- Problem proposed implementations
- Recommend different approaches
- Apply software program design rules
This collaboration between the developer and the LLM is essential to constructing
maintainable and scalable methods. The LLM can assist generate working code,
however the developer is the one who could make it extra readable, maintainable and
scalable.
Instruments that deal with diagrams as code, akin to PlantUML, are invaluable for speaking
complicated system habits. Their text-based format simplifies versioning, automation, and
evolving architectural diagrams alongside code. In my work explaining distributed
methods, PlantUML’s sequence diagrams are notably helpful for capturing interactions
exactly.
Nevertheless, I typically wished for an extension to stroll via these diagrams step-by-step,
revealing interactions sequentially reasonably than exhibiting your entire complicated move at
as soon as—like a slideshow for execution paths. This want displays a typical developer
situation: wanting personalised extensions or inner instruments for their very own wants.
But, extending established instruments like PlantUML typically entails vital preliminary
setup—parsing hooks, construct scripts, viewer code, packaging—sufficient “plumbing” to
deter speedy prototyping. The preliminary funding required to start can suppress good
concepts.
That is the place Massive Language Fashions (LLMs) show helpful. They will deal with boilerplate
duties, liberating builders to deal with design and core logic. This text particulars how I
used an LLM to construct PlantUMLSteps, a small extension including step-wise
playback to PlantUML sequence diagrams. The purpose is not simply the device itself, however
illustrating the method how syntax design, parsing, SVG era, construct automation,
and an HTML viewer have been iteratively developed via a dialog with an LLM,
turning tedious duties into manageable steps.
Diagram as code – A PlantUML primer
Earlier than diving into the event course of, let’s briefly introduce PlantUML
for many who is perhaps unfamiliar. PlantUML is an open-source device that enables
you to create UML diagrams from a easy text-based description language. It
helps
numerous diagram varieties together with sequence, class, exercise, element, and state
diagrams.
The ability of PlantUML lies in its capacity to model management diagrams
as plain textual content, combine with documentation methods, and automate diagram
era inside improvement pipelines. That is notably helpful for
technical documentation that should evolve alongside code.
Here is a easy instance of a sequence diagram in PlantUML syntax:
@startuml cover footbox actor Consumer participant System participant Database Consumer -> System: Login Request System --> Consumer: Login Type Consumer -> System: Submit Credentials System -> Database: Confirm Credentials Database --> System: Validation Consequence System --> Consumer: Authentication Consequence Consumer -> System: Request Dashboard System -> Database: Fetch Consumer Knowledge Database --> System: Consumer Knowledge System --> Consumer: Dashboard View @enduml
When processed by PlantUML, this textual content generates a visible sequence diagram exhibiting the
interplay between parts.

The code-like nature of PlantUML makes
it straightforward to be taught and use, particularly for builders who’re already snug
with text-based instruments.
This simplicity is what makes PlantUML an ideal candidate for extension. With the
proper tooling, we are able to improve its capabilities whereas sustaining its text-based
workflow.
Our purpose for this undertaking is to create a device which may divide the
sequence diagram into steps and generate a step-by-step view of the diagram.
So for the above diagram, we should always be capable to view login, authentication and
dashboard
steps one after the other.
Step 2: Constructing the Parser Logic (and Debugging)
“Now we have to parse the plantuml information and separate out step. At any time when we
encounter a step marker, we create a step object and preserve including the following strains
to it till we encounter one other step marker or finish of file. In case we
encounter one other step counter, we create new step object, it ought to have all
the contains, actors and contributors from the earlier step. It must also
have all of the content material of the earlier step, until the step metadata has
‘newPage’ attribute. If there aren’t any step markers encountered, which is the case
the place we have now information with out steps, it ought to create a default step. Create a
StepParser to parse given puml information and create checklist of steps.”
Claude generated the preliminary code for a StepParser class and a Step mannequin class to
deal with parsing PlantUML information with step markers. The preliminary implementation had some
logical points:
- Incorrect dealing with of step content material inheritance when newPage attribute was false
- Improper dealing with of declarations (actors, contributors) showing earlier than the
first step marker - Points with making a default step for information with out markers
The Cursor editor was operating in Agent mode, so after operating assessments and figuring out
these points via the failure messages, Claude offered a corrected model that
correctly dealt with:
- Content material collected earlier than step one marker
- Inheritance of content material from the instantly previous step
- World monitoring of declarations throughout steps
- Correct creation of a default step for information with out markers
With these corrections, the parser efficiently handed all assessments.
The following step was to generate a gradle process.
We’d like gradle process which may course of puml information in src/diagrams and its sub
folders. For every file it ought to create a listing with the title of the file the place
it generates legitimate puml file for every step. It will possibly generate that by simply including
@startuml at the beginning and @enduml on the finish of the step content material.
I am going to assist you to create a Gradle process to course of PlantUML information and generate
step-by-step diagrams. First, let’s create the duty in
construct.gradle:
// Course of every .puml file within the enter listing and its subdirectories
fileTree(inputDir).embody('**/*.puml').every { pumlFile ->
def relativePath = inputDir.toPath().relativize(pumlFile.toPath()).toString()
def fileName = pumlFile.title.exchange('.puml', '')
def stepOutputDir = new File(outputDir, fileName)
if (!stepOutputDir.exists()) {
stepOutputDir.mkdirs()
}
// Run the generator for this file
javaexec {
classpath = sourceSets.most important.runtimeClasspath
mainClass = 'com.instance.StepDiagramGenerator'
args = [pumlFile.absolutePath, stepOutputDir.absolutePath]
}
Claude additionally helped producing a easy plantuml sequence diagram to check the gradle
process. The identical one which we used in the beginning of the article.
The gradle process wanted a category PlantUMLGenerator which
can generate SVGs for every step.
Cursor within the Agent mode generated the code for the category.
It then ran the construct to confirm the duty.
Let's run a take a look at to substantiate our implementation works: cd /Customers/unmeshjoshi/work/plantumlsequence && ./gradlew clear construct
Job :generateStepDiagrams
Generated step diagram: /Customers/unmeshjoshi/work/plantumlsteps/construct/generated-diagrams/user-authentication/step-01-step-1-user-login.puml
Generated step diagram: /Customers/unmeshjoshi/work/plantumlsteps/construct/generated-diagrams/user-authentication/step-02-step-2-authentication.puml
Generated step diagram: /Customers/unmeshjoshi/work/plantumlsteps/construct/generated-diagrams/user-authentication/step-03-step-3-dashboard.puml
Generated step move abstract: /Customers/unmeshjoshi/work/plantumlsteps/construct/generated-diagrams/user-authentication/abstract.puml
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 543ms
3 actionable duties: 3 executed
Step 3: Producing HTML Viewer for Step Sequence
The following step was to generate a easy HTML viewer that can be utilized to view the step
sequence.
Now we have to generate a HTML viewer for the step information to be proven one after the other.
The HTML viewer can have a view space the place we present the svg picture generated for every
step with the step title within the metadata for that step. We will have subsequent and former
buttons to point out subsequent and former step picture.
I am going to assist you to create an HTML viewer for the step diagrams. We’ll must: Generate
SVG information from the PlantUML information Create an HTML viewer with navigation controls
Replace the Gradle process to generate each PlantUML and SVG information, together with the HTML
viewer First, let’s create a easy HTML template for the viewer:
….
The agent mode found out just a few points with the template however auto-fixed it by
operating some corrective actions.
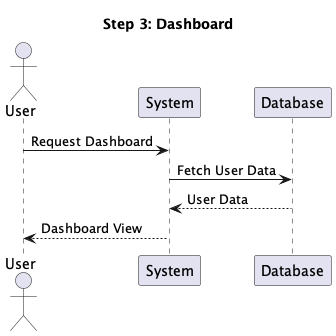
This setup allowed us to rapidly generate step diagrams from a single PlantUML file,
and consider them in a step-by-step method. So the above diagram might be seen as a
sequence of following steps:



The Code is the Supply of Fact
The place to go from right here?
Whereas the prompts and the LLM assistant (on this case, interacting in an agent-like
mode, using fashions like Claude Sonnet) offered a remarkably efficient solution to
generate a working first model of PlantUMLSteps, it is essential to
acknowledge the character of this generated output.
- Prompts will not be Deterministic: The prompts utilized in our dialog have been
efficient for this interplay, however they can’t be handled as the final word
‘supply of fact’. The identical prompts given to a unique mannequin, and even the identical
mannequin at a later date, will not be assured to provide the very same output due
to the inherent variability in LLM era. - Code Requires Administration: The generated code is the supply of fact for
the device’s performance. As such, it must be handled like some other
software program artifact – checked into model management, reviewed, examined, and
maintained. - Evaluation for Habitability: It is important to revisit the LLM-generated code
after the preliminary creation part. Is it ‘liveable’? That’s, is it moderately
straightforward to learn, perceive, and modify by a human developer? Whereas the LLM helped
overcome preliminary hurdles and boilerplate, making certain the long-term maintainability
and readability of the codebase typically requires human overview and potential
refactoring. The purpose is code that not solely works however can be advanced
successfully over time.
Prompting in pure language (like English) to generate code works nicely within the
early phases of improvement—while you’re exploring concepts, scaffolding performance,
or getting acquainted with a brand new device or framework. However as your system begins to take
form, the boundaries of obscure or broad prompts change into obvious. At this stage, what’s
wanted isn’t extra code era, however conceptual modeling—utilizing the constructs of
your programming language or know-how stack to precisely symbolize the area.
This stage wants deeper considering to construct abstractions, and an alignment between
code construction and area ideas—one thing solely achievable via considerate
design, not simply prompting. If prompt-based code era with out
overview is named “vibe coding,” then the extra disciplined method might be
known as “AI-assisted structured coding.”.
Past Code Technology: The Developer Perception in Refactoring
The following step was to refactor the code to make it extra readable and maintainable.
Initially, the parse technique was an extended, monolithic operate that dealt with every little thing
from
detecting step markers to managing declarations and content material. The code was troublesome
to
perceive and keep.
The complete code is offered in
this preliminary commit on GitHub.
The `StepParser.java` parse technique wants refactoring. It ought to symbolize ideas
used within the requirement or area ideas and observe customary clear code practices
with intentional technique names and code that reads like a DSL.
This preliminary request was open-ended, indicating that the developer acknowledged the
want for enchancment however was searching for steerage on tips on how to method it.
The LLM responded with a complete refactoring that launched a number of new
lessons and strategies:
- Launched `PlantUmlDocument` to symbolize the doc being parsed
- Smaller, extra targeted strategies with intention-revealing names
- Higher encapsulation of associated behaviors
- Extra expressive variable and technique names
/**
* Represents a PlantUML doc being parsed, managing state throughout parsing
*/
non-public class PlantUmlDocument {
non-public remaining Checklist steps = new ArrayList();
non-public remaining Checklist declarations = new ArrayList();
non-public remaining Checklist contentBeforeFirstStep = new ArrayList();
non-public Step currentStep = null;
non-public boolean hasStepMarkers = false;
public void beginNewStep(StepMetadata metadata) {
hasStepMarkers = true;
// Save the present step if it exists
if (currentStep != null) {
steps.add(currentStep);
}
// Create a brand new step
currentStep = new Step(metadata.getName(), metadata.isNewPage(), metadata.getAttributes());
// Add all declarations to the brand new step
currentStep.addAllDeclarations(declarations);
// If this is not a brand new web page and we have now earlier steps, copy all content material from earlier steps
if (!metadata.isNewPage() && !steps.isEmpty()) {
carryOverPreviousStepsContent();
}
}
non-public void carryOverPreviousStepsContent() {
for (Step previousStep : steps) {
for (String contentLine : previousStep.getContent()) {
currentStep.addContent(contentLine);
}
}
}
public void addDeclaration(String line) {
declarations.add(line);
if (currentStep != null) {
currentStep.addDeclaration(line);
} else {
contentBeforeFirstStep.add(line);
}
}
public void addContentLine(String line) {
if (currentStep != null) {
currentStep.addContent(line);
} else if (!line.trim().isEmpty()) {
contentBeforeFirstStep.add(line);
}
}
public void finalizeDocument() {
// Add the final step if it exists and hasn't been added but
if (currentStep != null) {
steps.add(currentStep);
}
}
The complete code is offered in
this commit on GitHub.
The `contentBeforeFirstStep` in `PlantUmlDocument.java` is used just for creating
default step when there aren’t any step markers?
So we are able to presumably
do two go processing the place we first verify if there are step markers.. if there
are.. we do step-based processing. Or else we simply create a default step and add all
declarations and content material. That can take away the necessity to have `contentBeforeFirstStep`
We will additionally possibily title PlantUmlDocument as `ParsedPumlFile` which represents
the parsed puml file.
The LLM applied this suggestion with a two-pass method. It additionally renamed the
PlantUmlDocument as ParsedPumlFile.
The complete code is offered in
this commit on GitHub.
`ParsedPumlFile` might be higher represented as builder sample.
`StepBuilder` generally is a builder for `Step` objects.
This perception demonstrated the developer’s capacity to acknowledge design patterns,
noting that the refactored class adopted the Builder sample.
The ultimate refactoring represents a major enchancment over the unique code:
class StepBuilder {
non-public remaining Checklist steps = new ArrayList();
non-public remaining Checklist globalDeclarations = new ArrayList();
non-public Step currentStep = null;
public void startNewStep(StepMetadata metadata) {
if (currentStep != null) {
steps.add(currentStep);
}
currentStep = new Step(metadata);
currentStep.addAllDeclarations(globalDeclarations);
if (!metadata.isNewPage() && !steps.isEmpty()) {
// Copy content material from the earlier step
Step previousStep = steps.get(steps.dimension() - 1);
for (String contentLine : previousStep.getContent()) {
currentStep.addContent(contentLine);
}
}
}
public void addDeclaration(String declaration) {
globalDeclarations.add(declaration);
if (currentStep != null) {
currentStep.addDeclaration(declaration);
}
}
public void addContent(String content material) {
// If no step has been began but, create a default step
if (currentStep == null) {
StepMetadata metadata = new StepMetadata("Default Step", false, new HashMap());
startNewStep(metadata);
}
currentStep.addContent(content material);
}
public Checklist construct() {
if (currentStep != null) {
steps.add(currentStep);
}
return new ArrayList(steps);
}
}
The complete code is offered in
this commit on GitHub.
There are extra enhancements doable,
however I’ve included just a few to reveal the character of collaboration between LLMs
and builders.
Conclusion
Every a part of this extension—remark syntax, Java parsing logic, HTML viewer, and
Gradle wiring—began with a targeted LLM immediate. Some elements required some knowledgeable
developer steerage to LLM, however the important thing profit was with the ability to discover and
validate concepts with out getting slowed down in boilerplate. LLMs are notably
useful when you have got a design in thoughts however will not be getting began due to
the efforts wanted for organising the scaffolding to strive it out. They can assist
you generate working glue code, combine libraries, and generate small
UIs—leaving you to deal with whether or not the thought itself works.
After the preliminary working model, it was necessary to have a developer to information
the LLM to enhance the code, to make it extra maintainable. It was essential
for builders to:
- Ask insightful questions
- Problem proposed implementations
- Recommend different approaches
- Apply software program design rules
This collaboration between the developer and the LLM is essential to constructing
maintainable and scalable methods. The LLM can assist generate working code,
however the developer is the one who could make it extra readable, maintainable and
scalable.