The infamous Lazarus Group, a North Korean state-backed hacking group, is again at it once more. This time, they’re sneaking malicious code into the favored npm software program repository, a significant useful resource for numerous builders worldwide.
Cybersecurity researchers at Socket Analysis Workforce have discovered six new faux packages, already downloaded round 330 instances, designed to infiltrate builders’ computer systems, swipe login particulars, steal cryptocurrency info, and even set up a backdoor for long-term entry.
What’s npm and Why Ought to I Care?
Consider npm as a large on-line library for JavaScript code. Builders use it to seize pre-built items of software program (referred to as “packages”) to save lots of effort and time when constructing their very own purposes. If a hacker can sneak a foul bundle into this library, they’ll infect anybody who downloads and makes use of it.
The Sneaky Ways of The Lazarus Group
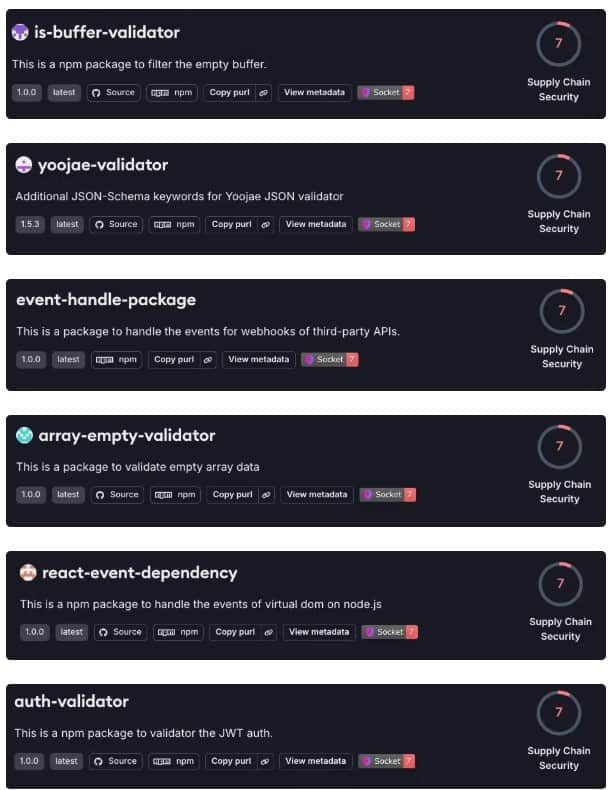
The Lazarus Group is utilizing “typosquatting” in its newest marketing campaign, creating packages with names very just like professional, widely-used ones. For instance, they created “is-buffer-validator,” which sounds loads like the true “is-buffer” bundle. This makes it simple for builders to unintentionally obtain the unsuitable factor.
Different malicious packages embrace yoojae-validator, event-handle-package, array-empty-validator, react-event-dependency, and auth-validator.
In accordance with Socket Analysis Workforce’s weblog put up, to make these faux packages look much more reliable, the hackers even arrange faux GitHub pages for a few of them. GitHub is the place builders usually share and collaborate on code, so having a presence there provides a layer of (false) legitimacy.
As Ensar Seker, CSO at cybersecurity firm SOCRadar, factors out, “Malicious npm packages are a very efficient assault vector as a result of builders usually belief open-source repositories with out thorough scrutiny.” He provides that attackers are “embedding malicious code in dependencies, making certain the malware spreads each time an unsuspecting developer installs or updates the bundle.”
What Occurs Upon An infection
The Lazarus Group has a historical past of concentrating on builders by provide chain assaults. On this marketing campaign, the malware embedded in compromised packages performs a number of malicious actions. It steals delicate knowledge by gathering system particulars such because the hostname, working system, and listing buildings. Moreover, it extracts credentials by looking out browser profiles for saved login info from Chrome, Courageous, and Firefox.
The malware additionally targets cryptocurrency wallets, particularly looking for Solana (id.json) and Exodus (exodus.pockets) pockets recordsdata to steal crypto belongings. Moreover, it installs a backdoor by downloading extra malware, together with the InvisibleFerret backdoor, which permits attackers to keep up persistent entry to the compromised system.
Seker notes that the concentrate on cryptocurrency aligns with North Korea’s identified methods. “The truth that these packages are designed to steal cryptocurrency-related knowledge aligns with North Korea’s state-backed cybercrime aims, which contain monetary theft to fund regime actions,” he explains. “Lazarus has a protracted historical past of concentrating on crypto wallets, exchanges, and fintech firms.”
The implications lengthen past particular person builders. “As soon as put in, these backdoored packages might give Lazarus entry to developer credentials, SSH keys, and cloud entry tokens,” Seker warns, “permitting lateral motion throughout complete organizations, not simply particular person victims.”
All Malicious Packages Deleted, however the Menace Stays
The excellent news is that GitHub has deleted all of the malicious packages recognized and reported by the Socket Analysis Workforce. Nonetheless, this doesn’t imply that there aren’t any different malicious packages operated by the Lazarus Group.
The way to Shield Your self and Your Group
To mitigate the dangers posed by provide chain assaults, each builders and organizations ought to undertake proactive safety measures. Builders ought to confirm bundle sources by checking the writer’s popularity and obtain numbers earlier than set up.
Using safety instruments, such because the Socket AI Scanner, may help detect malicious dependencies earlier than they’re added to a challenge. Moreover, enabling multi-layered safety by implementing sandboxing, endpoint safety, and blocking suspicious outbound connections provides an additional layer of defence.
Organizations can additional improve safety by automating dependency auditing to usually scan third-party packages for vulnerabilities. Monitoring dependency modifications and establishing alerts for surprising updates in initiatives may help detect potential threats early. Lastly, educating groups about typosquatting and coaching builders to acknowledge suspicious bundle names is vital in stopping assaults.